6.3 KiB
Gearman based test queue for refstack.org
launchpad blueprint: https://blueprints.launchpad.net/refstack/+spec/refstack-org-gearman-tester
Set up gearman worker/client for triggering official test runs from refstack.org
- build gearman client / job monitor
- stand alone worker script that does not require that refstack is installed.
- Test status reporting API call
- package installer for test runner with dependency and version coverage.
Problem description
In an effort to make this hostable long term and scalable, we need a way to manage a queue of tests that run on a distributed infrastructure. For that I like gearman.
This covers the Public cloud vendor official testing use case.
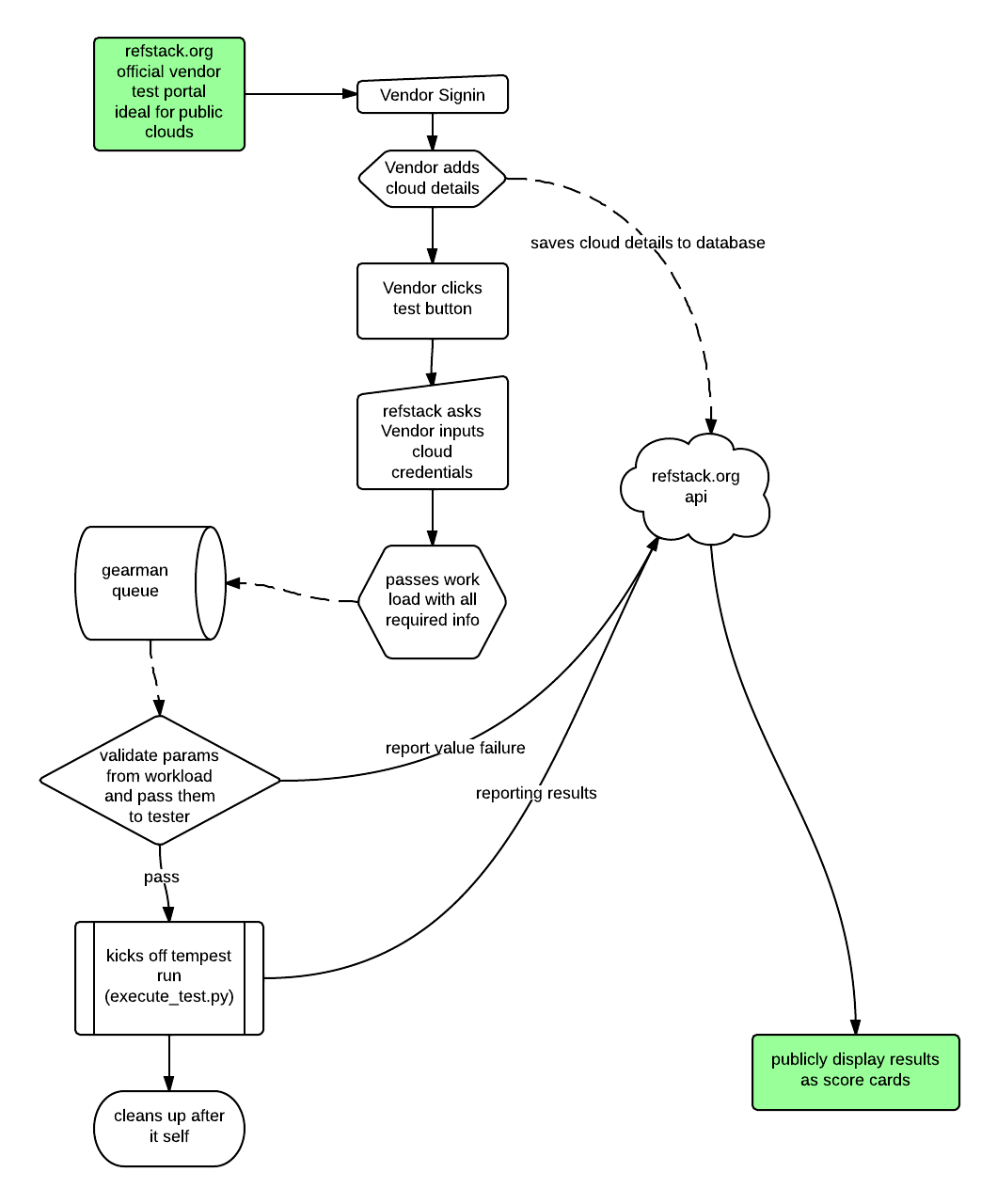
Proposed change
Generalized gearman flow.
- execute_test.py is already installed on gearman worker node.
- The run_gearman method in tempest_tester.py will use gearman client to send over a payload.
- The payload will have the necessary information to construct the arguments to execute_test.py
- Gearman worker receives the payload.
- Validates the payload Sets up local virtual env and installs the correct version of tempest within it.
- The worker then kicks off execute_test with -callback
refstack servertest_id--conf_jsonfrom payload--tempest_hometempest install dir - With the current execute_test.py code, it will interact with the refstack server to get more information about the cloud being tested to construct the tempest.config, and get the testcases to be run (optional), then execute the tempest test from the tempest_home. At the end, it will automatically send back the results to Refstack server.
Note: with this design, gearman worker will have network access to the Refstack server and will need access to the cloud being tested.
This spec covers the following deliverables;
- gearman client side code. (https://review.opendev.org/84270/)
- gearman worker code (wip)
- Parts of this are already stubbed out in the code. specifically the "run_gearman" method.
- Test status reporting API call
- This feature will overlap with the following blue print: https://blueprints.launchpad.net/refstack/+spec/update-test-status
- Installer with dependency coverage for the worker to improve speed of deployment of new workers.
- In this instance tempest would be installed in a virtual env before every test. So that the exact version of tempest that is needed for this specific test is installed in a way that is easy to clean up afterwards for the next test that will run on that worker node.
Alternatives
There are a lot of other job queue type things .. I happen to love gearman and the infra team has a gearman based system in place already.. they know how to troubleshoot it and tweak it for performance.
Data model impact
This uses the current models without any changes.
REST API impact
- update-test-status
-
This is a basic method for remote testers to report status to the gui/api
- Method type: POST
- if result is accepted responds with 202
- Expected error http response code(s)
- 400 bad request.. parameter was missing?
- 405 not authorized, this method should only allow failure reports from known testing hosts
- URL: /update-test-status/
- Parameters
- payload - the payload object that was passed into the worker to
begin with
- on docker tests I think we should still post back from data if we can..
- test_id - the test id
- payload - the payload object that was passed into the worker to
begin with
Security impact
- Does this change touch sensitive data such as tokens, keys, or user data? NO
- Does this change alter the API in a way that may impact security, such as a new way to access sensitive information or a new way to login? NO
- Does this change involve cryptography or hashing? NO
- Does this change require the use of sudo or any elevated privileges? NO
- Does this change involve using or parsing user-provided data? This could be directly at the API level or indirectly such as changes to a cache layer. YES
- Can this change enable a resource exhaustion attack, such as allowing a single API interaction to consume significant server resources? Some examples of this include launching subprocesses for each connection, or entity expansion attacks in XML. NO (thats why we use gearman)
Notifications impact
The gearman client should be able to feed back its status updates to the 'TestStatus' model through the update-test-status method.
Other end user impact
Aside from the API, are there other ways a user will interact with this feature?
Users will be able to trigger, cancel, and, receive status updates.
Performance Impact
The idea behind using gearman for this is that we can scale the worker pool in and out depending on demand. So there is no real need to worry about performance impacts.
Other deployer impact
- using the gearman testing option will require two settings in refstack.cfg GEARMAN_SERVER and GEARMAN_PORT will need to be set with the location and port of the gearmand server.
- This change will require being enabled in the same file with the TEST_METHOD value set to "gearman".
Developer impact
TDB
Implementation
Assignee(s)
- Primary assignee:
-
dlenwell
- Other contributors:
-
rockyg (documentation) * these documents are ripe with raw material for docs :)
Work Items
- gearman client side code. (https://review.opendev.org/84270/)
-
- starts/stops/handle the gearman job queue
- gearman worker code (wip)
- report failure api call
- package installer for test runner with dependency coverage.
Dependencies
- extends openstack-infra/gear
will also require a running gearmand service someplace accessible to both worker and client.
Testing
TBD
Documentation Impact
This should already be included in the high level architecture documentation for refstack.