* use python3 * do not use install_rally.sh script * check centos-8 * remove postgres packages brom bindep Change-Id: I00abce40d333352b25848cfe941f845746bffa8c |
||
|---|---|---|
| .zuul.d | ||
| devstack | ||
| doc | ||
| etc | ||
| rally | ||
| rally-jobs | ||
| samples | ||
| tests | ||
| .coveragerc | ||
| .dockerignore | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .gitreview | ||
| bindep.txt | ||
| CHANGELOG.rst | ||
| CONTRIBUTING.rst | ||
| install_rally.sh | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| optional-requirements.txt | ||
| README.rst | ||
| requirements.txt | ||
| setup.cfg | ||
| setup.py | ||
| test-requirements.txt | ||
| tox.ini | ||
| upper-constraints.txt | ||
Rally
Rally is tool & framework that allows one to write simple plugins and combine them in complex tests scenarios that allows to perform all kinds of testing!
Team and repository tags
What is Rally
Rally is intended to provide a testing framework that is capable to perform specific, complicated and reproducible test cases on real deployment scenarios.
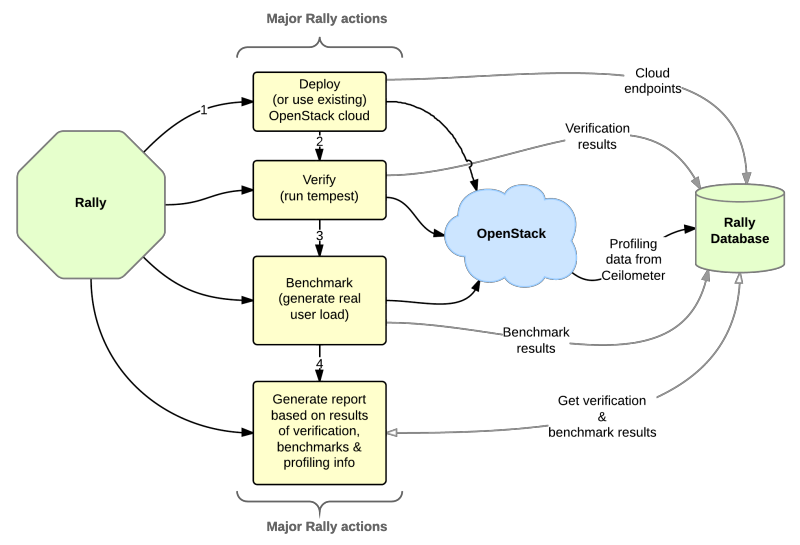
Rally workflow can be visualized by the following diagram:
Who Is Using Rally
Documentation
Rally documentation on ReadTheDocs is a perfect place to start learning about Rally. It provides you with an easy and illustrative guidance through this benchmarking tool.
For example, check out the Rally step-by-step tutorial that explains, in a series of lessons, how to explore the power of Rally in benchmarking your OpenStack clouds.
Architecture
In terms of software architecture, Rally is built of 4 main components:
- Environment - one of key component in Rally. It manages and stores information about tested platforms. Env manager is using platform plugins to: create, delete, cleanup, check health, obtain information about platforms.
- Task component is responsible for executing tests defined in task specs, persisting and reporting results.
- Verification component allows to wrap subunit-based testing tools and provide complete tool on top of them with allow to do pre configuration, post cleanup as well process and persist results to Rally DB for future use like reporting and results comparing.
Use Cases
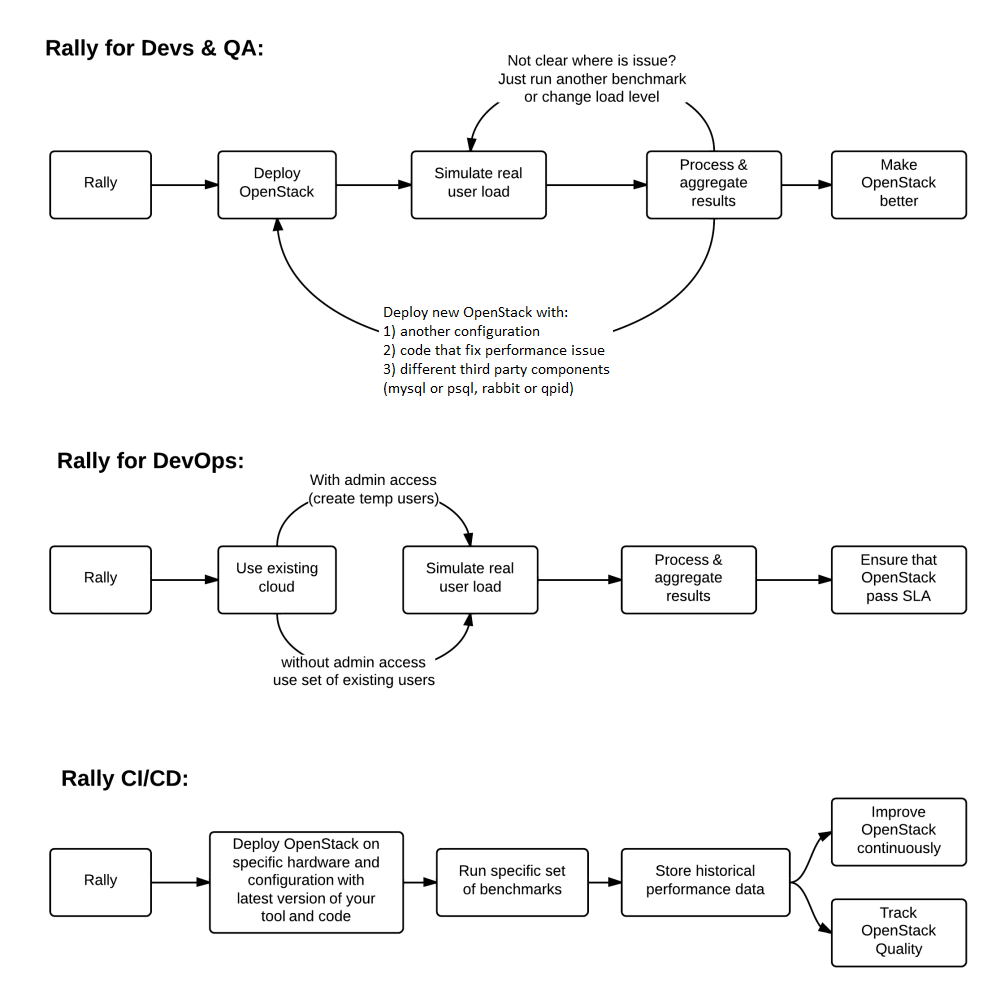
There are 3 major high level Rally Use Cases:
Typical cases where Rally aims to help are:
Automate measuring & profiling focused on how new code changes affect the OpenStack performance;
Using Rally profiler to detect scaling & performance issues;
Investigate how different deployments affect the OS performance:
- Find the set of suitable OpenStack deployment architectures;
- Create deployment specifications for different loads (amount of controllers, swift nodes, etc.);
Automate the search for hardware best suited for particular OpenStack cloud;
Automate the production cloud specification generation:
- Determine terminal loads for basic cloud operations: VM start & stop, Block Device create/destroy & various OpenStack API methods;
- Check performance of basic cloud operations in case of different loads.
Links
- Free software: Apache license
- Documentation: https://rally.readthedocs.org/en/latest/
- Source: https://opendev.org/openstack/rally
- Bugs: https://bugs.launchpad.net/rally
- Step-by-step tutorial: https://rally.readthedocs.io/en/latest/quick_start/tutorial.html
- Launchpad page: https://launchpad.net/rally
- Gitter chat: https://gitter.im/rally-dev/Lobby
- Trello board: https://trello.com/b/DoD8aeZy/rally