2.9 KiB
Enable SR-IOV
Prerequisites
This guide assumes that you have installed
Fuel and performed steps 5.3.1 - 5.3.9 from /install_guide. To enable
SR-IOV, you need a SRIOV-capable network PCI card. Also, only compute
hosts can be configured with theSRIOV role.
Features
- You can have multple VLANs inside one physical network
- When using
Passthrough, as in SR-IOV scenario, OpenStack does not provides dhcp and metadata. You have to manage that manually or provide an additional network port with a regular OpenStack network.
SR-IOV Description
Quoting Mirantis blog post:
SR-IOV is a PCI Special Interest Group (PCI-SIG) specification for virtualizing network interfaces, representing each physical resource as a configurable entity (called a PF for Physical Function), and creating multiple virtual interfaces (VFs or Virtual Functions) with limited configurability on top of it, recruiting support for doing so from the system BIOS, and conventionally, also from the host OS or hypervisor. Among other benefits, SR-IOV makes it possible to run a very large number of network-traffic-handling VMs per compute without increasing the number of physical NICs/ports and provides means for pushing processing for this down into the hardware layer, off-loading the hypervisor and significantly improving both throughput and deterministic network performance.
Verify SR-IOV environment
To verify if network interface is SRIOV-capable and how many VFs are available, run the following command on the boostraped host:
lspci -s <bus ID> -vvvEnable SR-IOV in Fuel
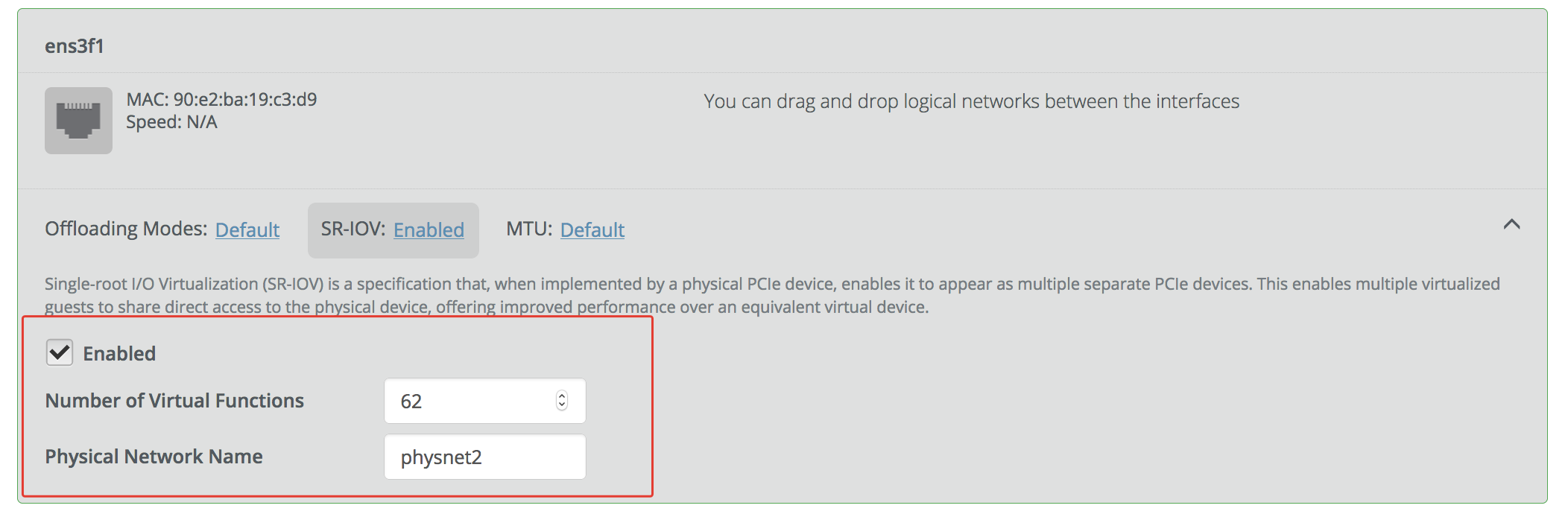
To enable SR-IOV in Fuel go to node interface configuration and enable it as shown on picture
- Deploy as in 5.3.10
/install_guide
Create a virtual machine with SR-IOV device
To create a virtual machine with SR-IOV device:
Create a VM with configured physical network and VLAN id:
neutron net-create \ --provider:physical_network=<physical network from contrail settings tab> \ --provider:segmentation_id=<Vlan_id> <Network_Name>Create a subnet:
neutron subnet-create <Network_name> <Subnet>Create a port:
neutron port-create \ --fixed-ip subnet_id=<subnet uuid>,ip_address=<IP address from above subnet> \ --name <name of port> <net uuid> --binding:vnic_type directBoot the VM with the port (use image with VF drivers, like Ubuntu or CentOS, Cirros will not work):
nova boot \ --flavor m1.large --image <image name> \ --nic port-id=<uuid of above port> <vm name>