- Added developer guide - Added installation guide - Removed screenshots of Horizon pages Change-Id: I827e9dad490099b7825ed812452d89fc7d4d0e83
5.2 KiB
Savanna Overview
Details
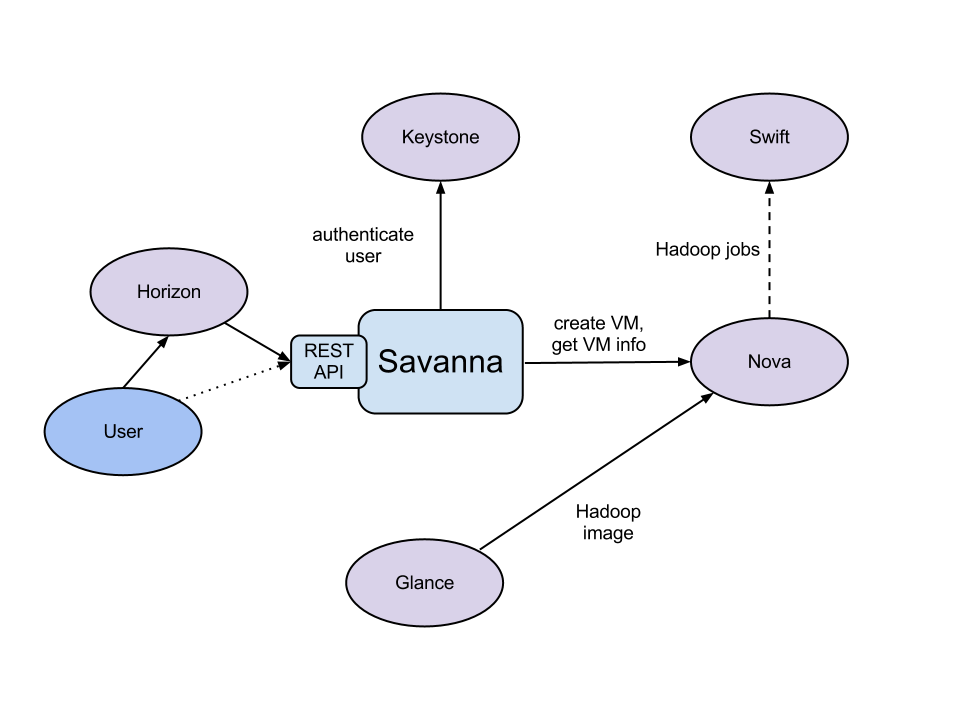
The Savanna product communicates with the following OpenStack components:
- Horizon - provides GUI with ability to use all of Savanna’s features;
- Keystone - authenticates users and provides security token that is used to work with the OpenStack, hence limiting user abilities in Savanna to his OpenStack privileges;
- Nova - is used to provision VMs for Hadoop Cluster;
- Glance - Hadoop VM images are stored there, each image containing an installed OS and Hadoop; the pre-installed Hadoop should give us good handicap on node start-up;
- Swift - can be used as a storage for data that will be processed by Hadoop jobs.
General Workflow
Savanna will provide two level of abstraction for API and UI based on the addressed use cases: cluster provisioning and analytics as a service.
For the fast cluster provisioning generic workflow will be as following:
select Hadoop version;
select base image with or without pre-installed Hadoop:
- for base images without Hadoop pre-installed Savanna will support pluggable deployment engines integrated with vendor tooling;
define cluster configuration, including size and topology of the cluster and setting the different type of Hadoop parameters (e.g. heap size):
- to ease the configuration of such parameters mechanism of configurable templates will be provided;
provision the cluster: Savanna will provision VMs, install and configure Hadoop;
operation on the cluster: add/remove nodes;
terminate the cluster when it’s not needed anymore.
For analytic as a service generic workflow will be as following:
select one of predefined Hadoop versions;
configure the job:
- choose type of the job: pig, hive, jar-file, etc.;
- provide the job script source or jar location;
- select input and output data location (initially only Swift will be supported);
- select location for logs;
set limit for the cluster size;
execute the job:
- all cluster provisioning and job execution will happen transparently to the user;
- cluster will be removed automatically after job completion;
get the results of computations (for example, from Swift).
User’s Perspective
While provisioning cluster through Savanna, user operates on two types of entities: Node Templates and Clusters.
Node Template describes a node within cluster and it has several parameters. Node Type is one of the Node Template’s properties that determines what Hadoop processes will be running on the node and thereby its role in the cluster. It could be either of JobTracker, NameNode, TaskTracker or DataNode, or any logical combination of these. Also template encapsulates hardware parameters (flavor) for the node VM and configuration for Hadoop processes running on the node.
Cluster entity simply represents Hadoop Cluster. It is mainly characterized by VM image with pre-installed Hadoop which will be used for cluster deployment and cluster topology. The topology is a list of node templates and respectively amount of nodes being deployed for each template. With respect to topology, Savanna checks only that cluster has one JobTracker and one NameNode.
Each node template and cluster belongs to some tenant determined by user. Users have access only to objects located in tenants they have access to. Users could edit/delete only objects they created. Naturally admin users have full access to every object. That way Savanna complies with general OpenStack access policy.
Savanna provides several kinds of Hadoop cluster topology. JobTracker and NameNode processes could be run either on a single VM or two separate ones. Also cluster could contain worker nodes of different types. Worker nodes could run both TaskTracker and DataNode, or either of these processes alone. Savanna allows user to create cluster with any combination of these options.
Integration with Swift
The Swift service is a standard object storage in OpenStack environment, analog of Amazon S3. As a rule it is deployed on bare metal machines. It is natural to expect Hadoop on OpenStack to process data stored there. There are a couple of enhancements on the way which can help there.
First, a FileSystem implementation for Swift: HADOOP-8545. With that thing in place, Hadoop jobs can work with Swift as naturally as with HDFS.
On the Swift side, we have the change request: Change I6b1ba25b (merged). It implements the ability to list endpoints for an object, account or container, to make it possible to integrate swift with software that relies on data locality information to avoid network overhead.
Pluggable Deployment and Monitoring
In addition to the monitoring capabilities provided by vendor-specific Hadoop management tooling, Savanna will provide pluggable integration with external monitoring systems such as Nagios or Zabbix.
Both deployment and monitoring tools will be installed on stand-alone VMs, thus allowing a single instance to manage/monitor several clusters at once.