This change moves the .rst files into the main adming-guide-cloud folder now conversion is complete. changes to the project config and to the openstack manuals to stop sync of .xml files are also needed. Change-Id: I498e8d6ac3cb80da413e23b14a0959abd58e7d79 Implements: blueprint reorganise-user-guides
1.5 KiB
1.5 KiB
Object Storage characteristics
The key characteristics of Object Storage are that:
- All objects stored in Object Storage have a URL.
- All objects stored are replicated 3✕ in as-unique-as-possible zones, which can be defined as a group of drives, a node, a rack, and so on.
- All objects have their own metadata.
- Developers interact with the object storage system through a RESTful HTTP API.
- Object data can be located anywhere in the cluster.
- The cluster scales by adding additional nodes without sacrificing performance, which allows a more cost-effective linear storage expansion than fork-lift upgrades.
- Data doesn't have to be migrate to an entirely new storage system.
- New nodes can be added to the cluster without downtime.
- Failed nodes and disks can be swapped out without downtime.
- It runs on industry-standard hardware, such as Dell, HP, and Supermicro.
Object Storage (swift)
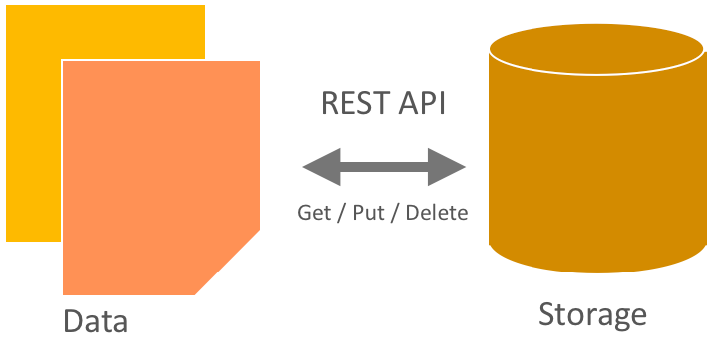
Developers can either write directly to the Swift API or use one of the many client libraries that exist for all of the popular programming languages, such as Java, Python, Ruby, and C#. Amazon S3 and RackSpace Cloud Files users should be very familiar with Object Storage. Users new to object storage systems will have to adjust to a different approach and mindset than those required for a traditional filesystem.