Keep the sync target repo path "common-rst" as of now. Change-Id: I552d2c0a422c4824632b11fa273629004b889306
1.7 KiB
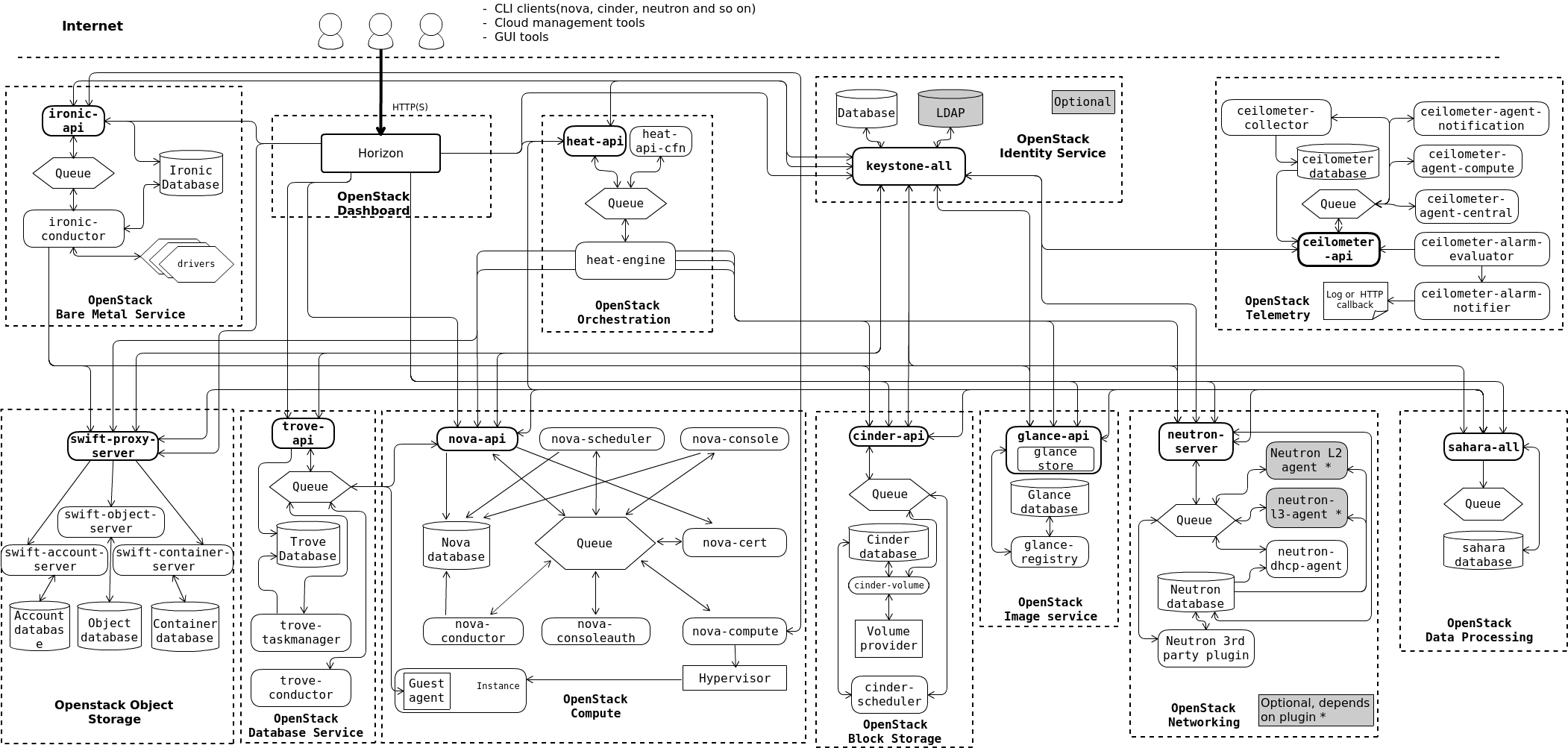
Logical architecture
To design, deploy, and configure OpenStack, administrators must understand the logical architecture.
As shown in get_started_conceptual_architecture, OpenStack
consists of several independent parts, named the OpenStack services. All
services authenticate through a common Identity service. Individual
services interact with each other through public APIs, except where
privileged administrator commands are necessary.
Internally, OpenStack services are composed of several processes. All services have at least one API process, which listens for API requests, preprocesses them and passes them on to other parts of the service. With the exception of the Identity service, the actual work is done by distinct processes.
For communication between the processes of one service, an AMQP message broker is used. The service's state is stored in a database. When deploying and configuring your OpenStack cloud, you can choose among several message broker and database solutions, such as RabbitMQ, Qpid, MySQL, MariaDB, and SQLite.
Users can access OpenStack via the web-based user interface
implemented by the get_started_dashboard, via command-line clients
and by issuing API requests through tools like browser plug-ins or curl. For applications,
several SDKs are
available. Ultimately, all these access methods issue REST API calls to
the various OpenStack services.
The following diagram shows the most common, but not the only possible, architecture for an OpenStack cloud: