| bin | ||
| freezer | ||
| horizon_web_ui | ||
| specs | ||
| tests | ||
| .coveragerc | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .gitreview | ||
| .pylintrc | ||
| CREDITS.rst | ||
| FAQ.rst | ||
| INSTALL.rst | ||
| LICENSE.rst | ||
| MANIFEST.in | ||
| README.rst | ||
| requirements.txt | ||
| runtests.py | ||
| setup.py | ||
| test-requirements.txt | ||
| TODO.rst | ||
| tox.ini | ||
Freezer
Freezer is a Backup Restore DR as a Service platform that helps you to automate the data backup and restore process.
The following features are available:
- Backup your filesystem using point in time snapshot
- Strong encryption supported: AES-256-CFB
- Backup your file system tree directly (without volume snapshot)
- Backup your journaled MongoDB directory tree using lvm snap to swift
- Backup MySQL DB with lvm snapshot
- Restore your data from a specific date automatically to your file system
- Low storage consumption as the backup are uploaded as a stream
- Flexible backup policy (incremental and differential)
- Data is archived in GNU Tar format for file based incremental
- Multiple compression algorithm support (zlib, bzip2, xz)
- Remove old backup automatically according the provided parameters
- Multiple storage media support (Swift, local file system, ssh)
- Flush kernel buffered memory to disk
- Multi platform (Linux, Windows, *BSD, OSX)
- Manage multiple jobs (i.e. multiple backups on the same node)
- Synchronize backups and restore on multiple nodes
- Web user interface integrated with OpenStack Horizon
- Can execute scripts/commands before or after a job execution
Requirements
- OpenStack Swift Account (optional)
- python
- GNU Tar >= 1.26
- gzip, bzip2, xz
- OpenSSL
- python-swiftclient
- python-keystoneclient
- pymongo
- PyMySQL
- libmysqlclient-dev
- sync
- At least 128 MB of memory reserved for Freezer
Installation & Env Setup
Install required packages
Ubuntu / Debian
Swift client and Keystone client:
$ sudo apt-get install -y python-dev
$ sudo easy_install -U pipMongoDB backup:
$ sudo apt-get install -y python-pymongoMySQL backup:
$ sudo pip install pymysqlFreezer installation from Python package repo:
$ sudo pip install freezerOR:
$ sudo easy_install freezerThe basic Swift account configuration is needed to use freezer. Make sure python-swiftclient is installed.
Also the following ENV var are needed you can put them in ~/.bashrc:
export OS_REGION_NAME=region-a.geo-1
export OS_TENANT_ID=<account tenant>
export OS_PASSWORD=<account password>
export OS_AUTH_URL=https://region-a.geo-1.identity.hpcloudsvc.com:35357/v2.0
export OS_USERNAME=automationbackup
export OS_TENANT_NAME=automationbackup
$ source ~/.bashrcLet's say you have a container called freezer_foobar-container, by executing "swift list" you should see something like:
$ swift list
freezer_foobar-container-2
$These are just use case example using Swift in the HP Cloud.
Is strongly advised to use execute a backup using LVM snapshot, so freezer will execute a backup on point-in-time data. This avoid risks of data inconsistencies and corruption.
Windows
Install OpenSSL binaries from http://www.openssl.org/related/binaries.html and add it to Path:
Install sync binaries from https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/bb897438 and add it to Path
General packages:
> easy_install -U pip
> pip install freezerThe basic Swift account configuration is needed to use freezer. Make sure python-swiftclient is installed:
set OS_REGION_NAME=region-a.geo-1
set OS_TENANT_ID=<account tenant>
set OS_PASSWORD=<account password>
set OS_AUTH_URL=https://region-a.geo-1.identity.hpcloudsvc.com:35357/v2.0
set OS_USERNAME=automationbackup
set OS_TENANT_NAME=automationbackupUsage Example
Freezer will automatically add the prefix "freezer" to the container name, where it is provided by the user and doesn't already start with this prefix. If no container name is provided, the default is freezer_backups.
The execution arguments can be set from command line and/or config file in ini format. there's an example of the job config file available in freezer/freezer/specs/job-backup.conf.example. Command line options always override the same options in the config file.
Backup
The most simple backup execution is a direct file system backup:
$ sudo freezerc --file-to-backup /data/dir/to/backup
--container freezer_new-data-backup --backup-name my-backup-name
* On windows (need admin rights)*
> freezerc --action backup --mode fs --backup-name testwindows
--path-to-backup "C:\path\to\backup" --container freezer_windows
--log-file C:\path\to\log\freezer.logBy default --mode fs is set. The command would generate a compressed tar gzip file of the directory /data/dir/to/backup. The generated file will be segmented in stream and uploaded in the swift container called freezer_new-data-backup, with backup name my-backup-name
Now check if your backup is executing correctly looking at /var/log/freezer.log
Execute a MongoDB backup using lvm snapshot:
We need to check before on which volume group and logical volume our mongo data is. These information can be obtained as per following:
$ mount
[...]Once we know the volume where our Mongo data is mounted on, we can get the volume group and logical volume info:
$ sudo vgdisplay
[...]
$ sudo lvdisplay
[...]We assume our mongo volume is "/dev/mongo/mongolv" and the volume group is "mongo":
$ sudo freezerc --lvm-srcvol /dev/mongo/mongolv --lvm-dirmount /var/lib/snapshot-backup
--lvm-volgroup mongo --file-to-backup /var/lib/snapshot-backup/mongod_ops2
--container freezer_mongodb-backup-prod --exclude "*.lock" --mode mongo --backup-name mongod-ops2Now freezerc create a lvm snapshot of the volume /dev/mongo/mongolv. If no options are provided, default snapshot name is freezer_backup_snap. The snap vol will be mounted automatically on /var/lib/snapshot-backup and the backup meta and segments will be upload in the container mongodb-backup-prod with the name mongod-ops2.
Execute a file system backup using lvm snapshot:
$ sudo freezerc --lvm-srcvol /dev/jenkins/jenkins-home --lvm-dirmount
/var/snapshot-backup --lvm-volgroup jenkins
--file-to-backup /var/snapshot-backup --container freezer_jenkins-backup-prod
--exclude "\*.lock" --mode fs --backup-name jenkins-ops2MySQL backup require a basic configuration file. The following is an example of the config:
$ sudo cat /root/.freezer/db.conf
host = your.mysql.host.ip
user = backup
password = userpasswordEvery listed option is mandatory. There's no need to stop the mysql service before the backup execution.
Execute a MySQL backup using lvm snapshot:
$ sudo freezerc --lvm-srcvol /dev/mysqlvg/mysqlvol
--lvm-dirmount /var/snapshot-backup
--lvm-volgroup mysqlvg --file-to-backup /var/snapshot-backup
--mysql-conf /root/.freezer/freezer-mysql.conf--container
freezer_mysql-backup-prod --mode mysql --backup-name mysql-ops002Cinder backups
To make a cinder backup you should provide cinder-vol-id or cindernative-vol-id parameter in command line arguments. Freezer doesn't do any additional checks and assumes that making backup of that image will be sufficient to restore your data in future.
- Execute a cinder backup::
-
$ freezerc --cinder-vol-id 3ad7a62f-217a-48cd-a861-43ec0a04a78b
Execute a mysql backup with cinder:
$ freezerc --mysql-conf /root/.freezer/freezer-mysql.conf
--container freezer_mysql-backup-prod --mode mysql
--backup-name mysql-ops002
--cinder-vol-id 3ad7a62f-217a-48cd-a861-43ec0a04a78bNova backups
To make a nova backup you should provide nova parameter in arguments. Freezer doesn't do any additional checks and assumes that making backup of that instance will be sufficient to restore your data in future.
- Execute a nova backup::
-
$ freezerc --nova-inst-id 3ad7a62f-217a-48cd-a861-43ec0a04a78b
Execute a mysql backup with nova:
$ freezerc --mysql-conf /root/.freezer/freezer-mysql.conf
--container freezer_mysql-backup-prod --mode mysql
--backup-name mysql-ops002
--nova-inst-id 3ad7a62f-217a-48cd-a861-43ec0a04a78bAll the freezerc activities are logged into /var/log/freezer.log.
Local storage backup execution:
- $ sudo freezerc --file-to-backup /data/dir/to/backup
--container /my_backup_path/ --backup-name my-backup-name --storage local
Restore
As a general rule, when you execute a restore, the application that write or read data should be stopped.
There are 3 main options that need to be set for data restore
File System Restore:
Execute a file system restore of the backup name adminui.git:
$ sudo freezerc --action restore --container freezer_foobar-container-2
--backup-name adminui.git
--restore-from-host git-HP-DL380-host-001 --restore-abs-path
/home/git/repositories/adminui.git/
--restore-from-date "2014-05-23T23:23:23"MySQL restore:
Execute a MySQL restore of the backup name holly-mysql. Let's stop mysql service first:
$ sudo service mysql stopExecute Restore:
$ sudo freezerc --action restore --container freezer_foobar-container-2
--backup-name mysq-prod --restore-from-host db-HP-DL380-host-001
--restore-abs-path /var/lib/mysql --restore-from-date "2014-05-23T23:23:23"And finally restart mysql:
$ sudo service mysql startExecute a MongoDB restore of the backup name mongobigdata:
$ sudo freezerc --action restore --container freezer_foobar-container-2
--backup-name mongobigdata --restore-from-host db-HP-DL380-host-001
--restore-abs-path /var/lib/mongo --restore-from-date "2014-05-23T23:23:23"List remote containers:
$ sudo freezerc --action info -LList remote objects in container:
$ sudo freezerc --action info --container freezer_testcontainer -lRemove backups older then 1 day:
$ freezerc --action admin --container freezer_dev-test --remove-older-then 1 --backup-name dev-test-01Cinder restore currently creates a volume with content of saved one, but doesn't implement deattach of existing volume and attach the new one to the vm. You should implement this steps manually. To create new volume from existing content run next command:
Execute a cinder restore:
$ freezerc --action restore --cinder-inst-id 3ad7a62f-217a-48cd-a861-43ec0a04a78b
$ freezerc --action restore --cindernative-vol-id 3ad7a62f-217a-48cd-a861-43ec0a04a78bNova restore currently creates an instance with content of saved one, but the ip address of vm will be different as well as it's id.
Execute a nova restore:
$ freezerc --action restore --nova-inst-id 3ad7a62f-217a-48cd-a861-43ec0a04a78bLocal storage restore execution:
$ sudo freezerc --action restore --container /local_backup_storage/ --backup-name adminui.git --restore-from-host git-HP-DL380-host-001 --restore-abs-path /home/git/repositories/adminui.git/ --restore-from-date "2014-05-23T23:23:23" --storage local
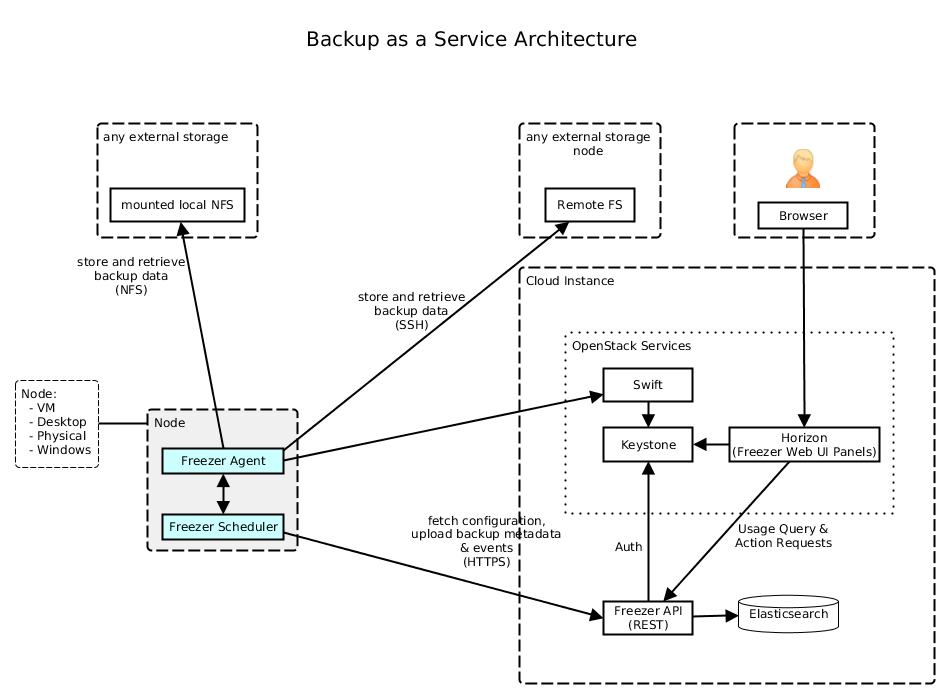
Architecture
Freezer architectural components are the following:
- OpenStack Swift (the storage)
- freezer client running on the node you want to execute the backups or restore
Freezer use GNU Tar under the hood to execute incremental backup and restore. When a key is provided, it uses OpenSSL to encrypt data (AES-256-CFB) ============= Freezer architecture is composed by the following components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
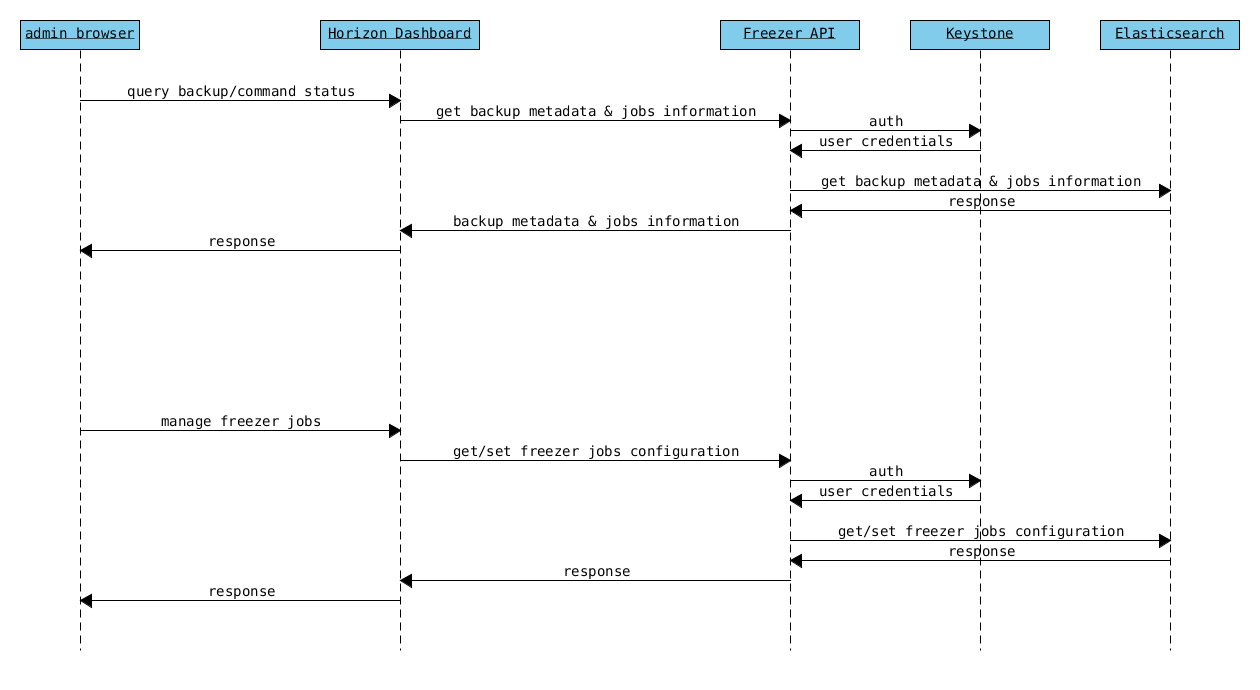
| Freezer Web UI | Web interface that interact with the Freezer API to configure, change settings. It provides most of the feature from the freezerc CLI, advanced scheduler settings as multi-node backup synchronization, metrics and reporting. |
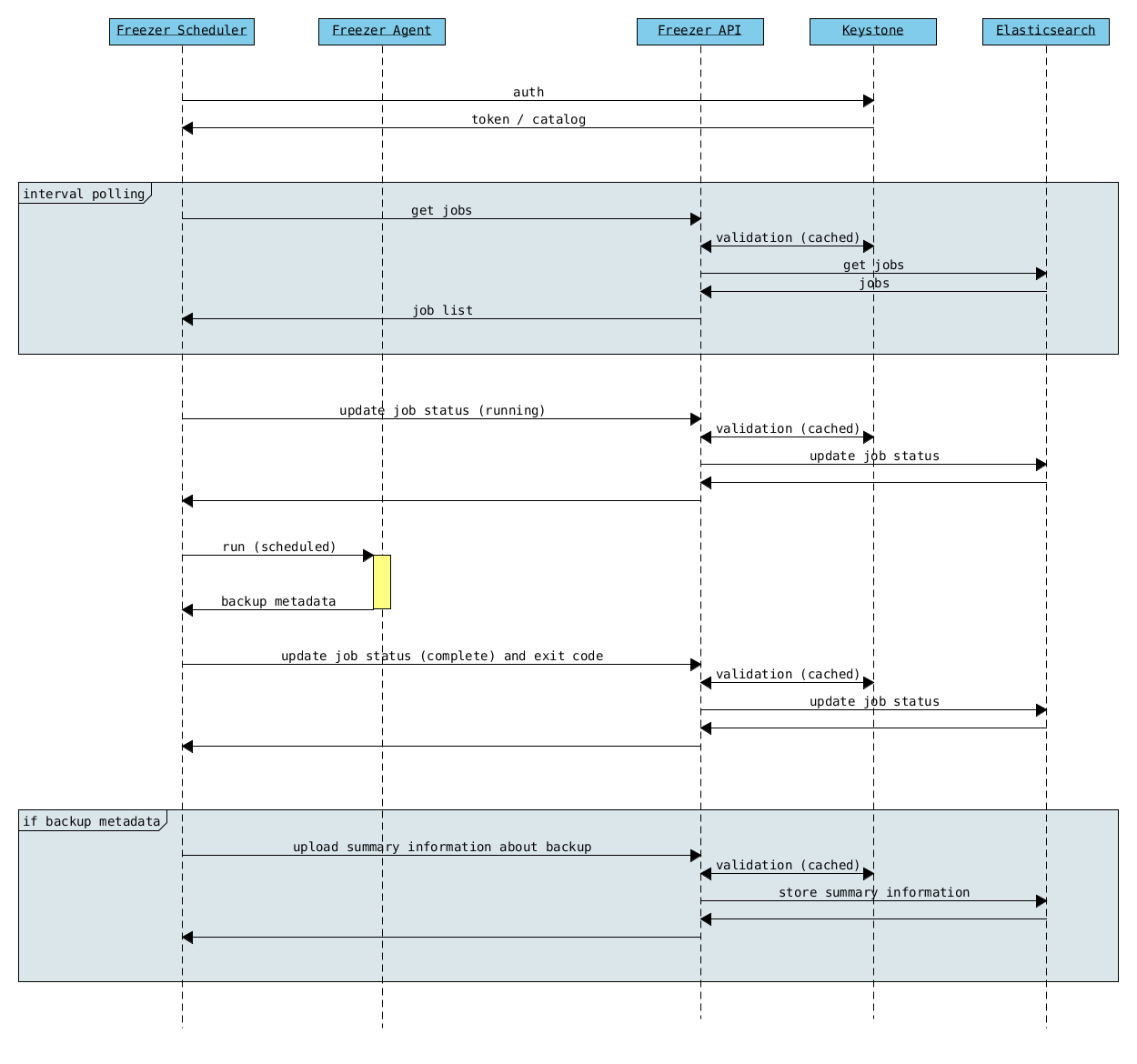
| Freezer Scheduler | A client side component, running on the node where the data backup has to be executed. It consist of a daemon that retrieve the data from the freezer API and execute jobs (i.e. backups, restore, admin actions, info actions, pre and/or post job scripts) by running the Freezer Agent. The metrics and exit codes returned by the freezer agent are captured and sent to the Freezer API. The scheduler manage the execution and synchronization of multiple jobs executed on a single or multiple nodes. The status of the execution of all the nodes is saved through the API. The Freezer scheduler take care of uploading jobs to the API by reading job files on the file system. It also have its own configuration file where job session or other settings like the freezer API polling interval can be configured. The Freezer scheduler manage jobs, for more information about jobs please refer to: freezer_api/README.rst under JOB the sections |
| Freezer Agent | Multiprocessing Python software that runs at client side, where the data backup has to be executed. It can be executed standalone or by the Freezer Scheduler. The freezerc provide flexible way to execute backup, restore and other actions on a running system. In order to provide flexibility in terms of data integrity, speed, performance, resources usage etc the freezer agent offer a wide range of options to execute optimized backup according the available resources as:
|
| Freezer API | API are used to store and provide metadata to the Freezer Web UI and to the Freezer Scheduler. Also the API are used to store session information for multi node backup synchronization. No workload data is stored in the API. For more information to the API please refer to: freezer_api/README.rst |
| DB Elasticsearch | Backend used by the API to store and retrieve metrics, metadata sessions information job status, etc. |
Freezer currently use GNU Tar under the hood to execute incremental backup and restore. When a key is provided, it uses OpenSSL to encrypt data (AES-256-CFB)
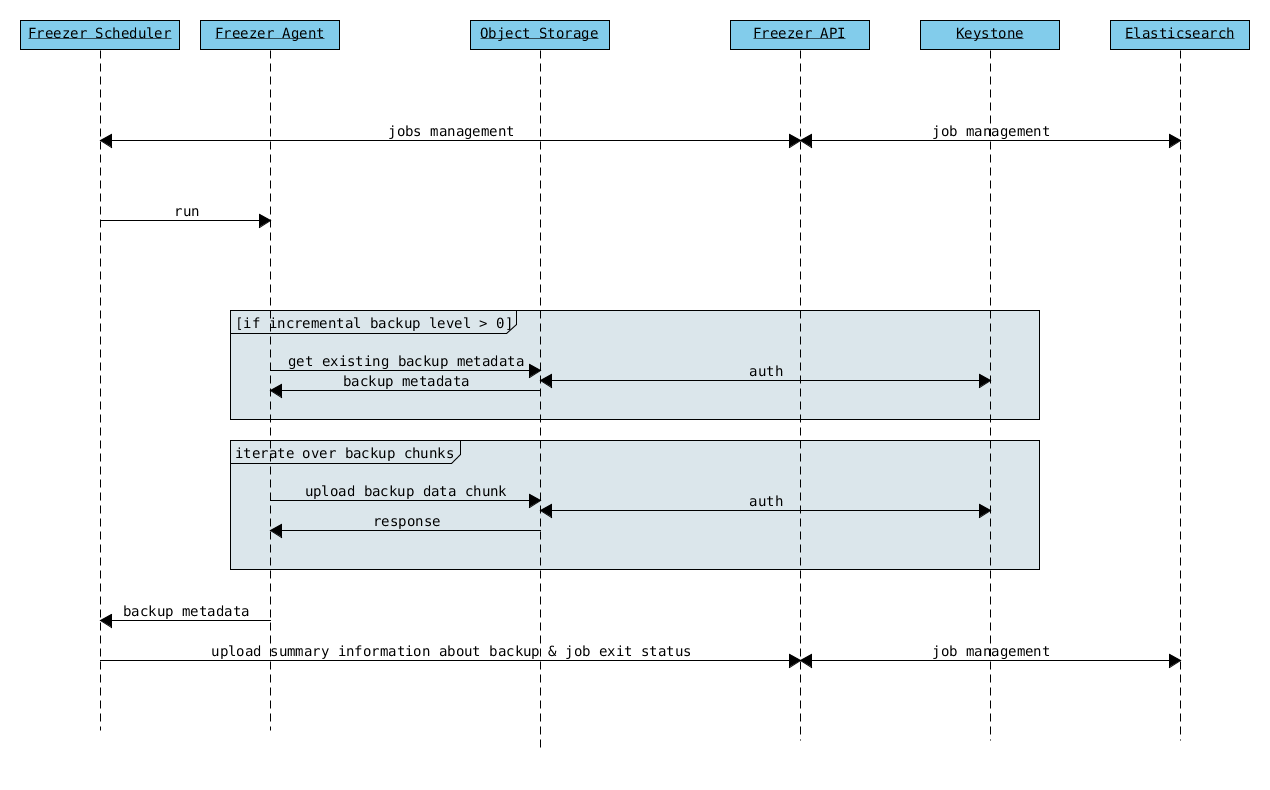
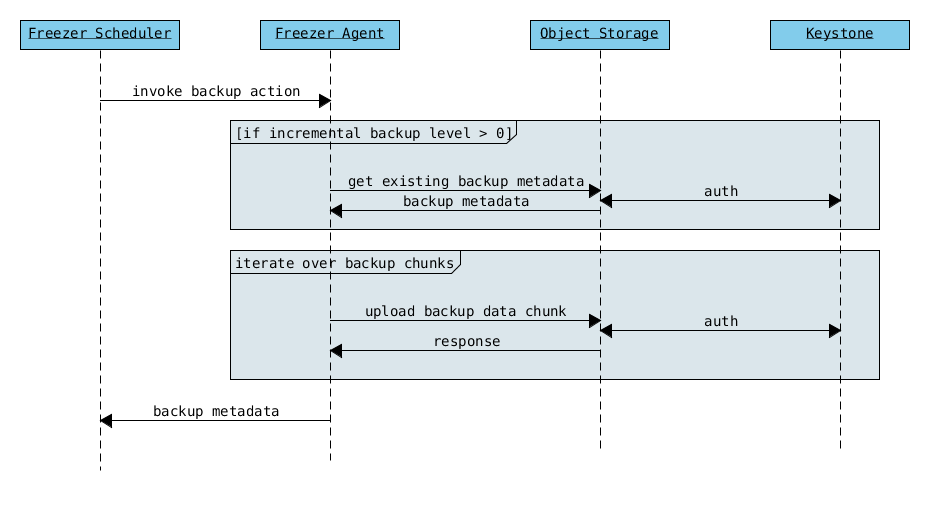
The following diagrams can help to better understand the solution:
Service Architecture
Freezer Agent backup work flow with API
Freezer Agent backup without API
Freezer Scheduler with API
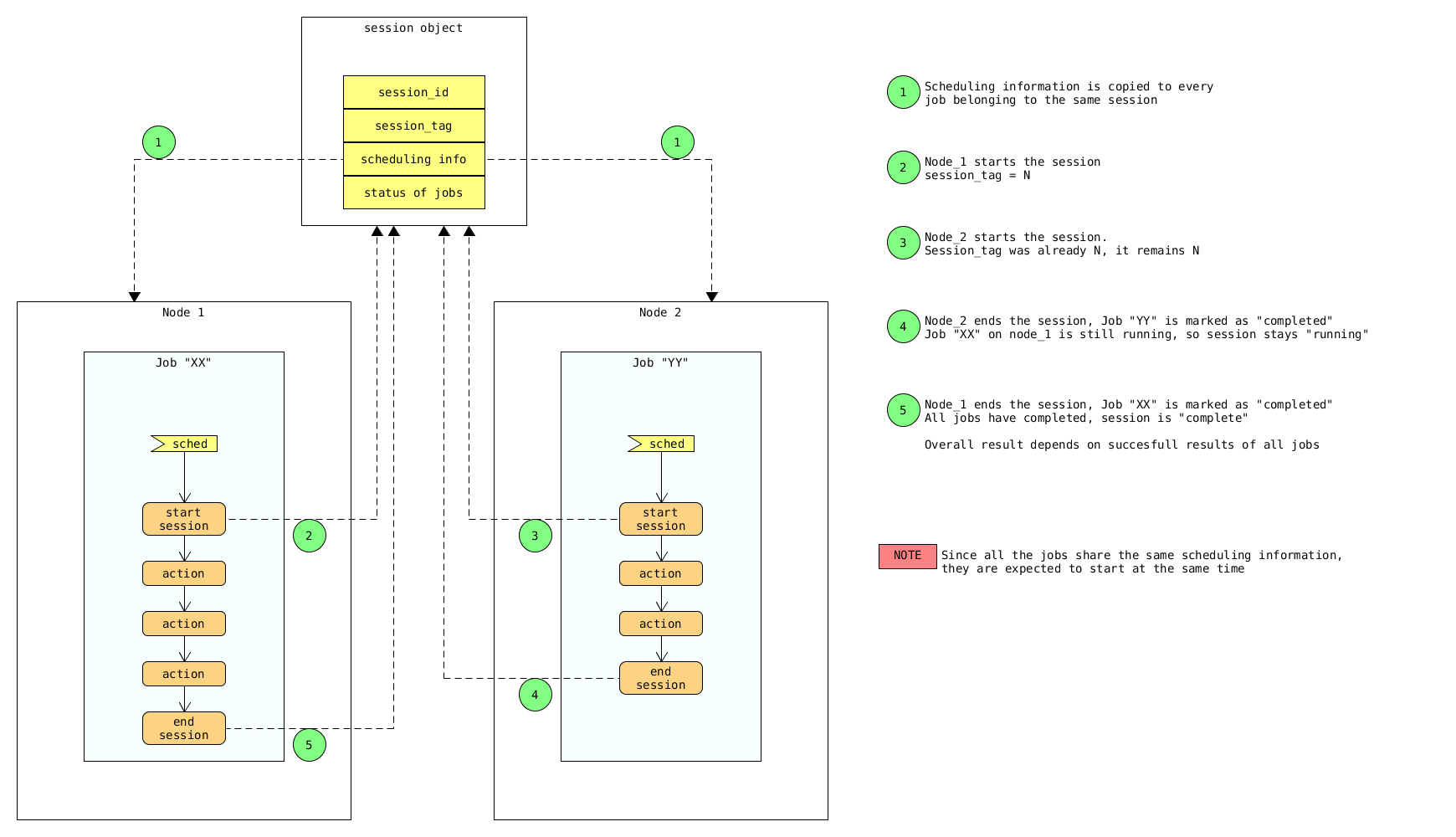
Freezer Job Session
Freezer Dashboard
How to scale
Low resources requirement
Freezer is designed to reduce at the minimum I/O, CPU and Memory Usage. This is achieved by generating a data stream from tar (for archiving) and gzip (for compressing). Freezer segment the stream in a configurable chunk size (with the option --max-seg-size). The default segment size is 64MB, so it can be safely stored in memory, encrypted if the key is provided, and uploaded to Swift as segment.
Multiple segments are sequentially uploaded using the Swift Manifest. All the segments are uploaded first, and then the Manifest file is uploaded too, so the data segments cannot be accessed directly. This ensue data consistency.
By keeping small segments in memory, I/O usage is reduced. Also as there's no need to store locally the final compressed archive (tar-gziped), no additional or dedicated storage is required for the backup execution. The only additional storage needed is the LVM snapshot size (set by default at 5GB). The lvm snapshot size can be set with the option --lvm-snapsize. It is important to not specify a too small snap size, because in case a quantity of data is being wrote to the source volume and consequently the lvm snapshot is filled up, then the data is corrupted.
If the more memory is available for the backup process, the maximum segment size can be increased, this will speed up the process. Please note, the segments must be smaller then 5GB, is that is the maximum object size in the Swift server.
Au contraire, if a server have small memory availability, the --max-seg-size option can be set to lower values. The unit of this option is in bytes.
How the incremental works
The incremental backups is one of the most crucial feature. The following basic logic happens when Freezer execute:
- Freezer start the execution and check if the provided backup name for the current node already exist in Swift
- If the backup exists, the Manifest file is retrieved. This is important as the Manifest file contains the information of the previous Freezer execution.
The following is what the Swift Manifest looks like:
{
'X-Object-Meta-Encrypt-Data': 'Yes',
'X-Object-Meta-Segments-Size-Bytes': '134217728',
'X-Object-Meta-Backup-Created-Timestamp': '1395734461',
'X-Object-Meta-Remove-Backup-Older-Than-Days': '',
'X-Object-Meta-Src-File-To-Backup': '/var/lib/snapshot-backup/mongod_dev-mongo-s1',
'X-Object-Meta-Maximum-Backup-level': '0',
'X-Object-Meta-Always-Backup-Level': '',
'X-Object-Manifest': u'socorro-backup-dev_segments/dev-mongo-s1-r1_mongod_dev-mongo-s1_1395734461_0',
'X-Object-Meta-Backup-Current-Level': '0',
'X-Object-Meta-Abs-File-Path': '',
'X-Object-Meta-Backup-Name': 'mongod_dev-mongo-s1',
'X-Object-Meta-Tar-Meta-Obj-Name': 'tar_metadata_dev-mongo-s1-r1_mongod_dev-mongo-s1_1395734461_0',
'X-Object-Meta-Hostname': 'dev-mongo-s1-r1',
'X-Object-Meta-Container-Segments': 'socorro-backup-dev_segments'
}- The most relevant data taken in consideration for incremental are:
- 'X-Object-Meta-Maximum-Backup-level': '7'
Value set by the option: --max-level int
Assuming we are executing the backup daily, let's say managed from the crontab, the first backup will start from Level 0, that is, a full backup. At every daily execution, the current backup level will be incremented by 1. Then current backup level is equal to the maximum backup level, then the backup restart to level 0. That is, every week a full backup will be executed.
- 'X-Object-Meta-Always-Backup-Level': ''
Value set by the option: --always-level int
When current level is equal to 'Always-Backup-Level', every next backup will be executed to the specified level. Let's say --always-level is set to 1, the first backup will be a level 0 (complete backup) and every next execution will backup the data exactly from the where the level 0 ended. The main difference between Always-Backup-Level and Maximum-Backup-level is that the counter level doesn't restart from level 0
- 'X-Object-Manifest': u'socorro-backup-dev/dev-mongo-s1-r1_mongod_dev-mongo-s1_1395734461_0'
Through this meta data, we can identify the exact Manifest name of the provided backup name. The syntax is: container_name/hostname_backup_name_timestamp_initiallevel
- 'X-Object-Meta-Backup-Current-Level': '0'
Record the current backup level. This is important as the value is incremented by 1 in the next freezer execution.
Value set by the option: -N BACKUP_NAME, --backup-name BACKUP_NAME The option is used to identify the backup. It is a mandatory option and fundamental to execute incremental backup. 'Meta-Backup-Name' and 'Meta-Hostname' are used to uniquely identify the current and next incremental backups
- 'X-Object-Meta-Tar-Meta-Obj-Name': 'tar_metadata_dev-mongo-s1-r1_mongod_dev-mongo-s1_1395734461_0'
Freezer use tar to execute incremental backup. What tar do is to store in a meta data file the inode information of every file archived. Thus, on the next Freezer execution, the tar meta data file is retrieved and download from swift and it is used to generate the next backup level. After the next level backup execution is terminated, the file update tar meta data file will be uploaded and recorded in the Manifest file. The naming convention used for this file is: tar_metadata_backupname_hostname_timestamp_backuplevel
- 'X-Object-Meta-Hostname': 'dev-mongo-s1-r1'
The hostname of the node where the Freezer perform the backup. This meta data is important to identify a backup with a specific node, thus avoid possible confusion and associate backup to the wrong node.
Nova and Cinder Backups
If our data is stored on cinder volume or nova instance disk, we can implement file backup using nova snapshots or volume backups.
Nova backups:
If you provide nova argument in parameters freezer assume that all necessary data is located on instance disk and it can be successfully stored using nova snapshot mechanism.
For example if we want to store our mysql located on instance disk, we will execute the same actions like in case of lvm or tar snapshots, but we will invoke nova snapshot instead of lvm or tar.
After that we will place snapshot to swift container as dynamic large object.
container/%instance_id%/%timestamp% <- large object with metadata container_segments/%instance_id%/%timestamp%/segments...
Restore will create a snapshot from stored data and restore an instance from this snapshot. Instance will have different id and old instance should be terminated manually.
Cinder backups:
Cinder has it's own mechanism for backups and freezer supports it. But it also allows create a glance image from volume and upload to swift.
To use standard cinder backups please provide --cindernative-vol-id argument.
Miscellanea
Please check the FAQ to: FAQ.rst
Available options:
$ freezerc
usage: freezerc [-h] [--config CONFIG] [--action {backup,restore,info,admin}]
[-F PATH_TO_BACKUP] [-N BACKUP_NAME] [-m MODE] [-C CONTAINER]
[-L] [-l] [-o GET_OBJECT] [-d DST_FILE]
[--lvm-auto-snap LVM_AUTO_SNAP] [--lvm-srcvol LVM_SRCVOL]
[--lvm-snapname LVM_SNAPNAME] [--lvm-snapsize LVM_SNAPSIZE]
[--lvm-dirmount LVM_DIRMOUNT] [--lvm-volgroup LVM_VOLGROUP]
[--max-level MAX_LEVEL] [--always-level ALWAYS_LEVEL]
[--restart-always-level RESTART_ALWAYS_LEVEL]
[-R REMOVE_OLDER_THAN] [--remove-from-date REMOVE_FROM_DATE]
[--no-incremental] [--hostname HOSTNAME]
[--mysql-conf MYSQL_CONF] [--log-file LOG_FILE]
[--exclude EXCLUDE]
[--dereference-symlink {none,soft,hard,all}] [-U]
[--encrypt-pass-file ENCRYPT_PASS_FILE] [-M MAX_SEGMENT_SIZE]
[--restore-abs-path RESTORE_ABS_PATH]
[--restore-from-host RESTORE_FROM_HOST]
[--restore-from-date RESTORE_FROM_DATE] [--max-priority] [-V]
[-q] [--insecure] [--os-auth-ver {1,2,3}] [--proxy PROXY]
[--dry-run] [--upload-limit UPLOAD_LIMIT]
[--cinder-vol-id CINDER_VOL_ID] [--nova-inst-id NOVA_INST_ID]
[--cindernative-vol-id CINDERNATIVE_VOL_ID]
[--download-limit DOWNLOAD_LIMIT]
[--sql-server-conf SQL_SERVER_CONF] [--vssadmin VSSADMIN]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--config CONFIG Config file abs path. Option arguments are provided
from config file. When config file is used any option
from command line provided take precedence.
--action {backup,restore,info,admin}
Set the action to be taken. backup and restore are
self explanatory, info is used to retrieve info from
the storage media, while admin is used to delete old
backups and other admin actions. Default backup.
-F PATH_TO_BACKUP, --path-to-backup PATH_TO_BACKUP, --file-to-backup PATH_TO_BACKUP
The file or directory you want to back up to Swift
-N BACKUP_NAME, --backup-name BACKUP_NAME
The backup name you want to use to identify your
backup on Swift
-m MODE, --mode MODE Set the technology to back from. Options are, fs
(filesystem), mongo (MongoDB), mysql (MySQL),
sqlserver (SQL Server) Default set to fs
-C CONTAINER, --container CONTAINER
The Swift container used to upload files to
-L, --list-containers
List the Swift containers on remote Object Storage
Server
-l, --list-objects List the Swift objects stored in a container on remote
Object Storage Server.
-o GET_OBJECT, --get-object GET_OBJECT
The Object name you want to download on the local file
system.
-d DST_FILE, --dst-file DST_FILE
The file name used to save the object on your local
disk and upload file in swift
--lvm-auto-snap LVM_AUTO_SNAP
Automatically guess the volume group and volume name
for given PATH.
--lvm-srcvol LVM_SRCVOL
Set the lvm volume you want to take a snaphost from.
Default no volume
--lvm-snapname LVM_SNAPNAME
Set the lvm snapshot name to use. If the snapshot name
already exists, the old one will be used a no new one
will be created. Default freezer_backup_snap.
--lvm-snapsize LVM_SNAPSIZE
Set the lvm snapshot size when creating a new
snapshot. Please add G for Gigabytes or M for
Megabytes, i.e. 500M or 8G. Default 5G.
--lvm-dirmount LVM_DIRMOUNT
Set the directory you want to mount the lvm snapshot
to. Default not set
--lvm-volgroup LVM_VOLGROUP
Specify the volume group of your logical volume. This
is important to mount your snapshot volume. Default
not set
--max-level MAX_LEVEL
Set the backup level used with tar to implement
incremental backup. If a level 1 is specified but no
level 0 is already available, a level 0 will be done
and subsequently backs to level 1. Default 0 (No
Incremental)
--always-level ALWAYS_LEVEL
Set backup maximum level used with tar to implement
incremental backup. If a level 3 is specified, the
backup will be executed from level 0 to level 3 and to
that point always a backup level 3 will be executed.
It will not restart from level 0. This option has
precedence over --max-backup-level. Default False
(Disabled)
--restart-always-level RESTART_ALWAYS_LEVEL
Restart the backup from level 0 after n days. Valid
only if --always-level option if set. If --always-
level is used together with --remove-older-then, there
might be the chance where the initial level 0 will be
removed Default False (Disabled)
-R REMOVE_OLDER_THAN, --remove-older-then REMOVE_OLDER_THAN, --remove-older-than REMOVE_OLDER_THAN
Checks in the specified container for object older
than the specified days.If i.e. 30 is specified, it
will remove the remote object older than 30 days.
Default False (Disabled) The option --remove-older-
then is deprecated and will be removed soon
--remove-from-date REMOVE_FROM_DATE
Checks the specified container and removes objects
older than the provided datetime in the form "YYYY-MM-
DDThh:mm:ss i.e. "1974-03-25T23:23:23". Make sure the
"T" is between date and time
--no-incremental Disable incremental feature. By default freezer build
the meta data even for level 0 backup. By setting this
option incremental meta data is not created at all.
Default disabled
--hostname HOSTNAME Set hostname to execute actions. If you are executing
freezer from one host but you want to delete objects
belonging to another host then you can set this option
that hostname and execute appropriate actions. Default
current node hostname.
--mysql-conf MYSQL_CONF
Set the MySQL configuration file where freezer
retrieve important information as db_name, user,
password, host, port. Following is an example of
config file: # cat ~/.freezer/backup_mysql_conf host =
<db-host> user = <mysqluser> password = <mysqlpass>
port = <db-port>
--log-file LOG_FILE Set log file. By default logs to
/var/log/freezer.logIf that file is not writable,
freezer tries to logto ~/.freezer/freezer.log
--exclude EXCLUDE Exclude files, given as a PATTERN.Ex: --exclude
'*.log' will exclude any file with name ending with
.log. Default no exclude
--dereference-symlink {none,soft,hard,all}
Follow hard and soft links and archive and dump the
files they refer to. Default False.
-U, --upload Upload to Swift the destination file passed to the -d
option. Default upload the data
--encrypt-pass-file ENCRYPT_PASS_FILE
Passing a private key to this option, allow you to
encrypt the files before to be uploaded in Swift.
Default do not encrypt.
-M MAX_SEGMENT_SIZE, --max-segment-size MAX_SEGMENT_SIZE
Set the maximum file chunk size in bytes to upload to
swift Default 67108864 bytes (64MB)
--restore-abs-path RESTORE_ABS_PATH
Set the absolute path where you want your data
restored. Default False.
--restore-from-host RESTORE_FROM_HOST
Set the hostname used to identify the data you want to
restore from. If you want to restore data in the same
host where the backup was executed just type from your
shell: "$ hostname" and the output is the value that
needs to be passed to this option. Mandatory with
Restore Default False.
--restore-from-date RESTORE_FROM_DATE
Set the absolute path where you want your data
restored. Please provide datetime in format "YYYY-MM-
DDThh:mm:ss" i.e. "1979-10-03T23:23:23". Make sure the
"T" is between date and time Default False.
--max-priority Set the cpu process to the highest priority (i.e. -20
on Linux) and real-time for I/O. The process priority
will be set only if nice and ionice are installed
Default disabled. Use with caution.
-V, --version Print the release version and exit
-q, --quiet Suppress error messages
--insecure Allow to access swift servers without checking SSL
certs.
--os-auth-ver {1,2,3}
Swift auth version, could be 1, 2 or 3
--proxy PROXY Enforce proxy that alters system HTTP_PROXY and
HTTPS_PROXY, use '' to eliminate all system proxies
--dry-run Do everything except writing or removing objects
--upload-limit UPLOAD_LIMIT
Upload bandwidth limit in Bytes per sec. Can be
invoked with dimensions (10K, 120M, 10G).
--cinder-vol-id CINDER_VOL_ID
Id of cinder volume for backup
--nova-inst-id NOVA_INST_ID
Id of nova instance for backup
--cindernative-vol-id CINDERNATIVE_VOL_ID
Id of cinder volume for native backup
--download-limit DOWNLOAD_LIMIT
Download bandwidth limit in Bytes per sec. Can be
invoked with dimensions (10K, 120M, 10G).
--sql-server-conf SQL_SERVER_CONF
Set the SQL Server configuration file where freezer
retrieve the sql server instance. Following is an
example of config file: instance = <db-instance>
--vssadmin VSSADMIN Create a backup using a snapshot on windows using
vssadmin. Options are: True and False, default is True